GST Outstanding: Monitor pending GST liabilities and dues for timely compliance.
GST Output: Track total GST collected on sales and outward supplies.
GST Input: View GST paid on purchases to manage input credit efficiently.
Payment Made: Review all payments processed against various expenses or liabilities.
Claim Outstanding Balance: Identify and reconcile pending claims across departments.
TDS Outstanding Balance: Check deducted but unpaid TDS amounts to ensure timely remittance.
Salary Outstanding Balance: Track unpaid or pending salary obligations.
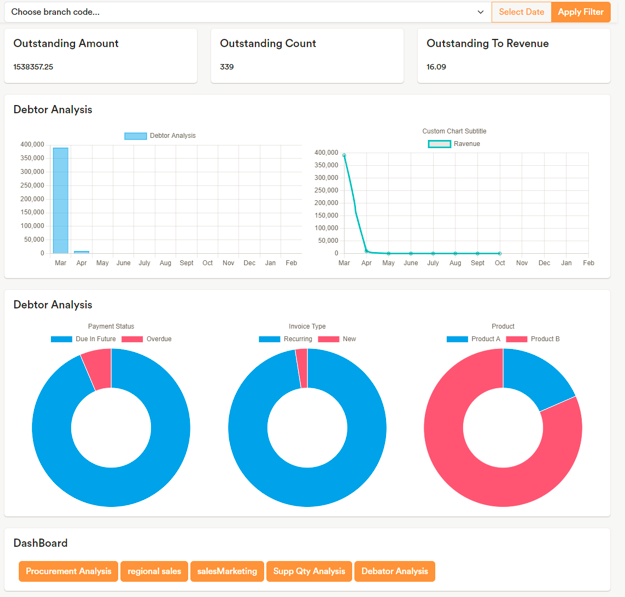
Accounts Receivable Outstanding: Monitor pending customer payments to improve cash flow.
Accounts Payable Outstanding: Manage dues owed to vendors for better financial planning.
Staff Outstanding Balance (Imprest): Keep track of advances given to staff and pending settlements.
MSME Outstanding Balance: Monitor payments due to MSME vendors to comply with statutory timelines.
MSME Overdue Balance: Highlight overdue MSME payments to avoid penalties.
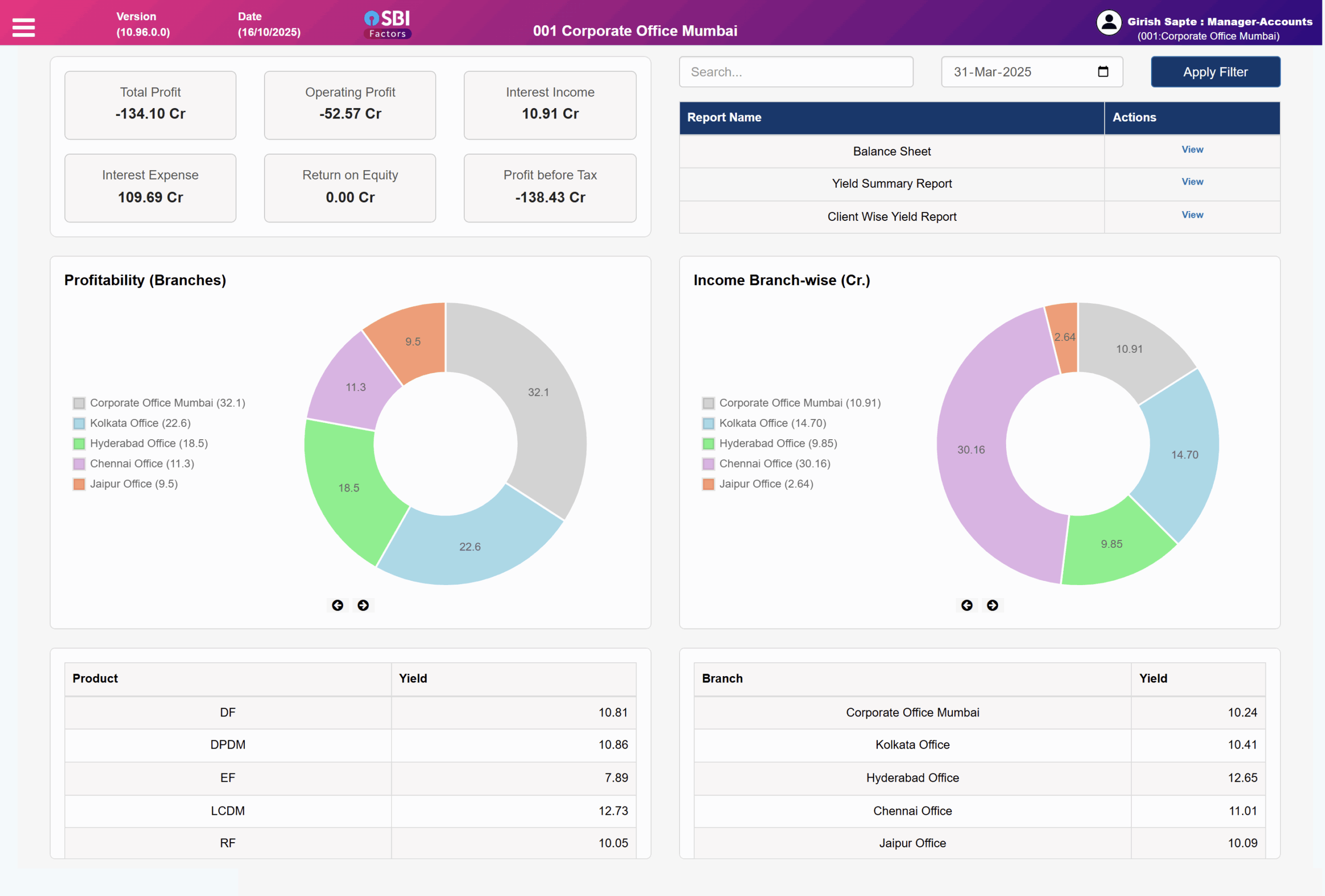
Total Profit: View overall profitability across the organization.
Operating Profit: Analyze profit generated from core operational activities.
Interest Income: Track revenue earned through interest on deposits or investments.
Interest Expense: Record and monitor interest paid on borrowings and loans.
Return on Equity: Evaluate business performance through equity-based profitability.
Profit Before Tax: Review financial performance before taxation impact.
Balance Sheet: Get a real-time snapshot of assets, liabilities, and equity.
Trial Balance: Verify accounting accuracy through consolidated debit-credit summary.
Day Book Reports: View day-to-day financial transactions across all vouchers.
Account Head Ledger: Access detailed ledgers for each account head for audit and analysis